Floating PV systems have emerged as a smart and sustainable solution for green energy production. But their long-term success relies on more than just panels and floats, it depends heavily on anchoring performance. Often invisible, the anchoring system is essential to ensure the stability, durability, and safety of the entire floating solar installation, resisting wind, waves, and water level variations.
In this article, we dive into the anchoring success factors for floating PV plants, from thorough site analysis and tailored anchoring design, to technology choices, materials, and long-term maintenance strategies.
Site assessment: the foundation of floating PV anchoring success
Assessing water body characteristics
The first success factor in floating solar anchoring lies in a deep knowledge of the site environment. Every reservoir, be it a lake, dam, quarry, or industrial basin, comes with unique constraints that influence the anchoring design. Surface area, water depth, shape, and fluctuation levels are all critical to determining the right anchoring method and layout.
Understanding soil composition
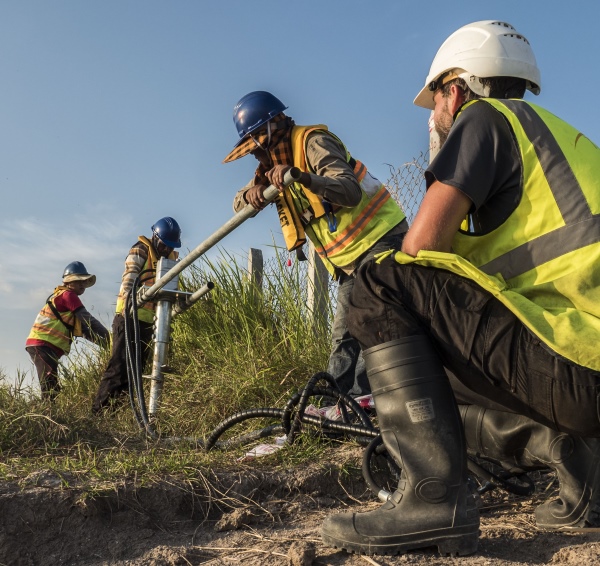
The soil at the bottom of the water body also plays a crucial role in the anchoring success of floating PV systems. It is essential to understand its composition to choose the most suitable type of anchor. Whether the soil is silty, sandy, clayey, or rocky, each type offers different resistance during anchor installation.
Geotechnical surveys allow project developers to determine the appropriate anchoring technology, such as:
- Screw anchors,
- Toggle (plate) anchors,
- Dead weights (concrete blocks),
- Chemical anchors, etc.
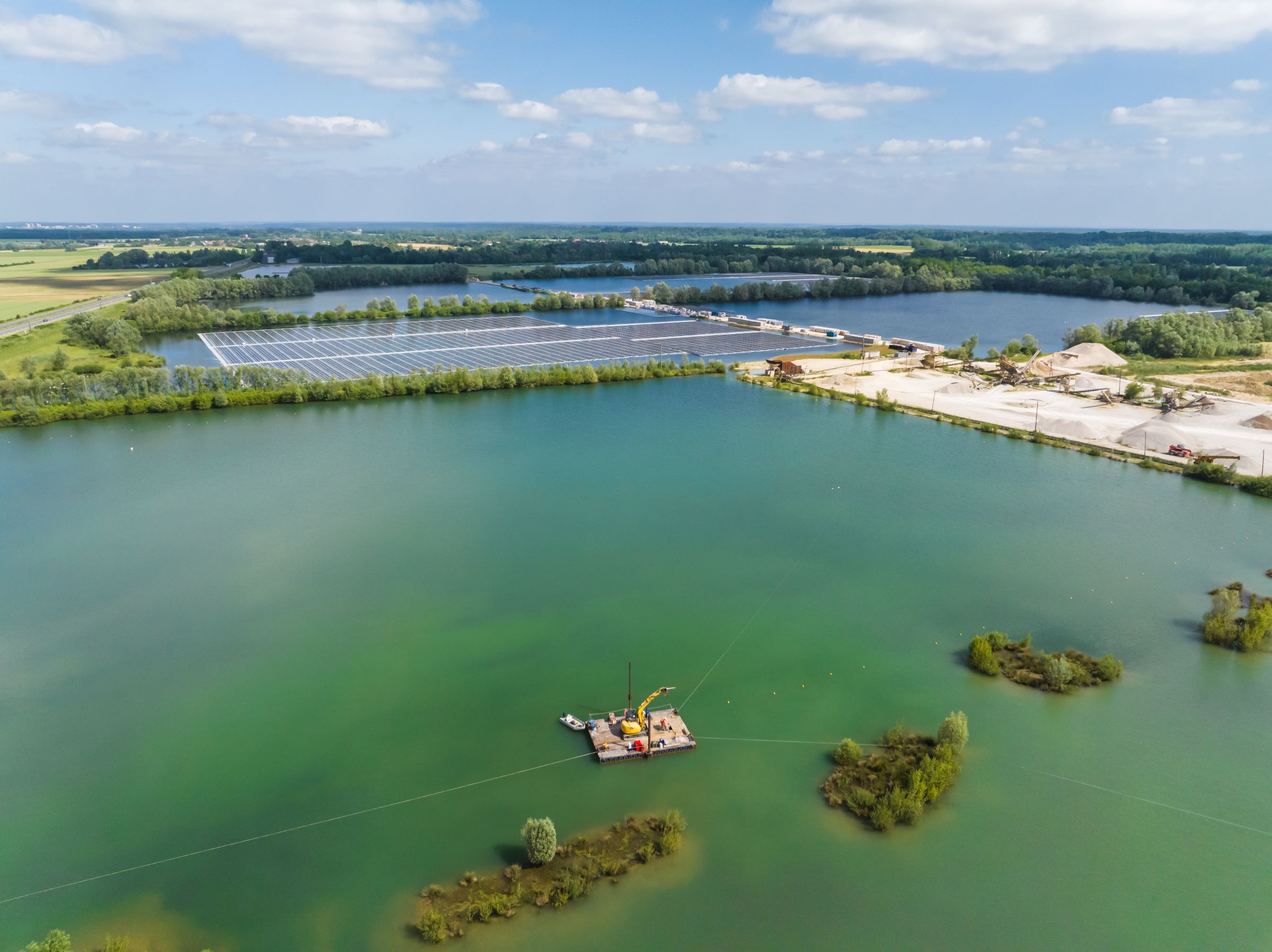
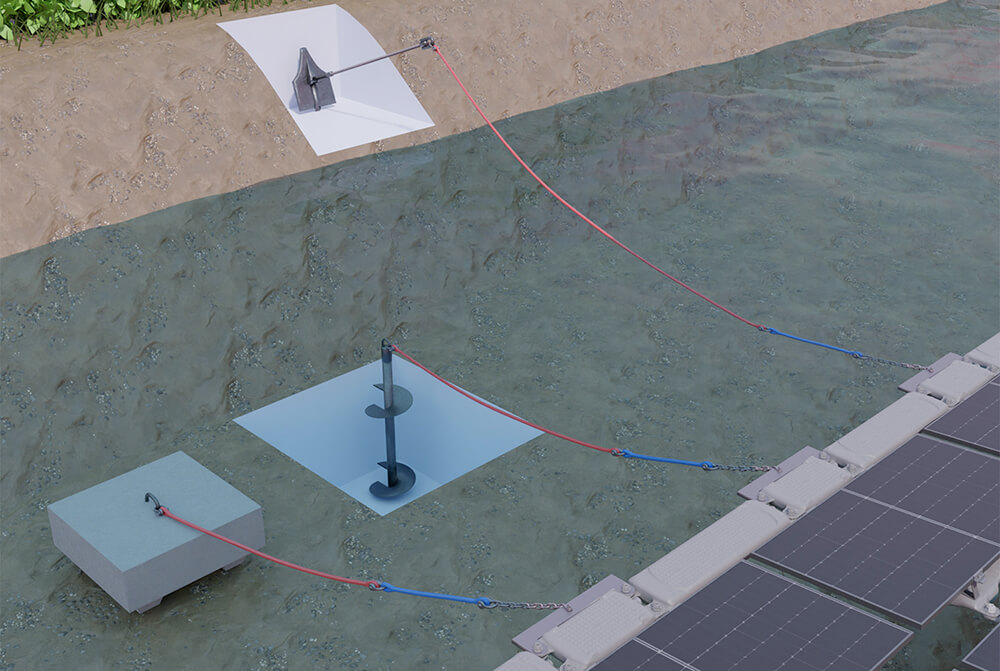

Analyzing environmental conditions, bathymetry, and topography
Bathymetry (depth mapping) and topography (bank mapping) are critical for determining:
- The appropriate lengths of mooring lines,
- Areas to avoid due to submerged obstacles,
- Emerged zones to bypass during low water levels,
- The feasibility of using bank anchoring, bottom anchoring, or a combination of both.
These data points directly influence the overall anchoring design for floating PV, including the positioning and accessibility of anchor points.
Additionally, climatic forces such as wind, current, and potential flooding must be anticipated during the design phase. On highly exposed sites, the anchoring system must absorb significant forces to avoid drifting or structural failure, making it one of the most essential anchoring success factors for floating solar.
A precise and site-specific anchoring design
The importance of technical sizing
Among the most critical anchoring success factors for floating PV is the accuracy of the system’s engineering design. This relies on advanced digital simulations, such as CFD (computational fluid dynamics) modeling, and detailed analysis of the mechanical forces acting on the floating array using site-specific data.
This process allows engineers to determine:
- The number of mooring lines required,
- Their lengths and arrangement,
- The mechanical load each line must withstand.
At Ciel & Terre, we base our anchoring design for floating PV on internationally recognized standards such as DNVGL-RP-0584 and Bureau Veritas NR493, ensuring a safe and reliable system. Our anchoring design methodology has also been certified by Bureau Veritas, reinforcing its credibility.
Mooring line types to address local constraints
Mooring lines are designed to manage both tensile forces and vertical movements caused by fluctuating water levels. The choice of materials depends on environmental conditions and includes:
- Polyester ropes,
- Galvanized chains,
- Stainless steel cables,
- Elastomeric materials, etc
This adaptability is essential to ensure that the anchoring system for floating PV remains effective under dynamic site conditions.
Selecting the right anchoring method: bottom, bank, or hybrid
Depending on site topography and lakebed characteristics, various anchoring methods may be used:
- Bottom anchoring: Anchors are fixed directly into the waterbed, using screw anchors, plate anchors, or concrete dead weights.


The appropriate anchoring method is determined based on the geometry and depth of the water body, banks accessibility, and both operational and environmental constraints.
Anchoring technologies and material selection: key to long-term durability
Anchoring technologies adapted to each soil type
Another essential anchoring success factor for floating solar is the selection of the right technology to fix mooring lines to the lakebed or banks. Common anchoring technologies include:
- Screw anchors: Ideal for cohesive soils such as clay, silt, or sand.
- Dead weights (concrete blocks): Suitable when it’s not possible to drill into the ground (e.g., presence of a liner or high groundwater).
- Plate anchors: Offer strong holding power in soft soils and are particularly resistant to currents and frequent water level changes.
- Steel piles (H-beams): Highly durable and typically used in large reservoirs or industrial zones, mainly along the shore.
- Pillars: Often installed in port areas or coastal bays to accommodate tidal water level fluctuations.
Each anchoring technology is selected during the design phase and aligned with bathymetric and geotechnical survey results to maximize the stability of the floating PV platform.
Materials built and selected to last 25+ years
The durability of the anchoring system depends significantly on the quality of materials used. Mooring lines and anchor components must withstand long-term mechanical fatigue, including repeated tension and relaxation cycles, for more than two decades. They must also resist:
- Corrosion in freshwater, brackish, or saltwater environments,
- UV radiation,
- Mechanical abrasion (e.g., from contact with hard sediments or floating debris),
- Environmental stresses from wind and current.

Material selection is therefore carried out with great care:
- Stainless or galvanized steel,
- High-performance synthetic ropes and textiles.
This careful selection is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability of floating solar anchoring systems.
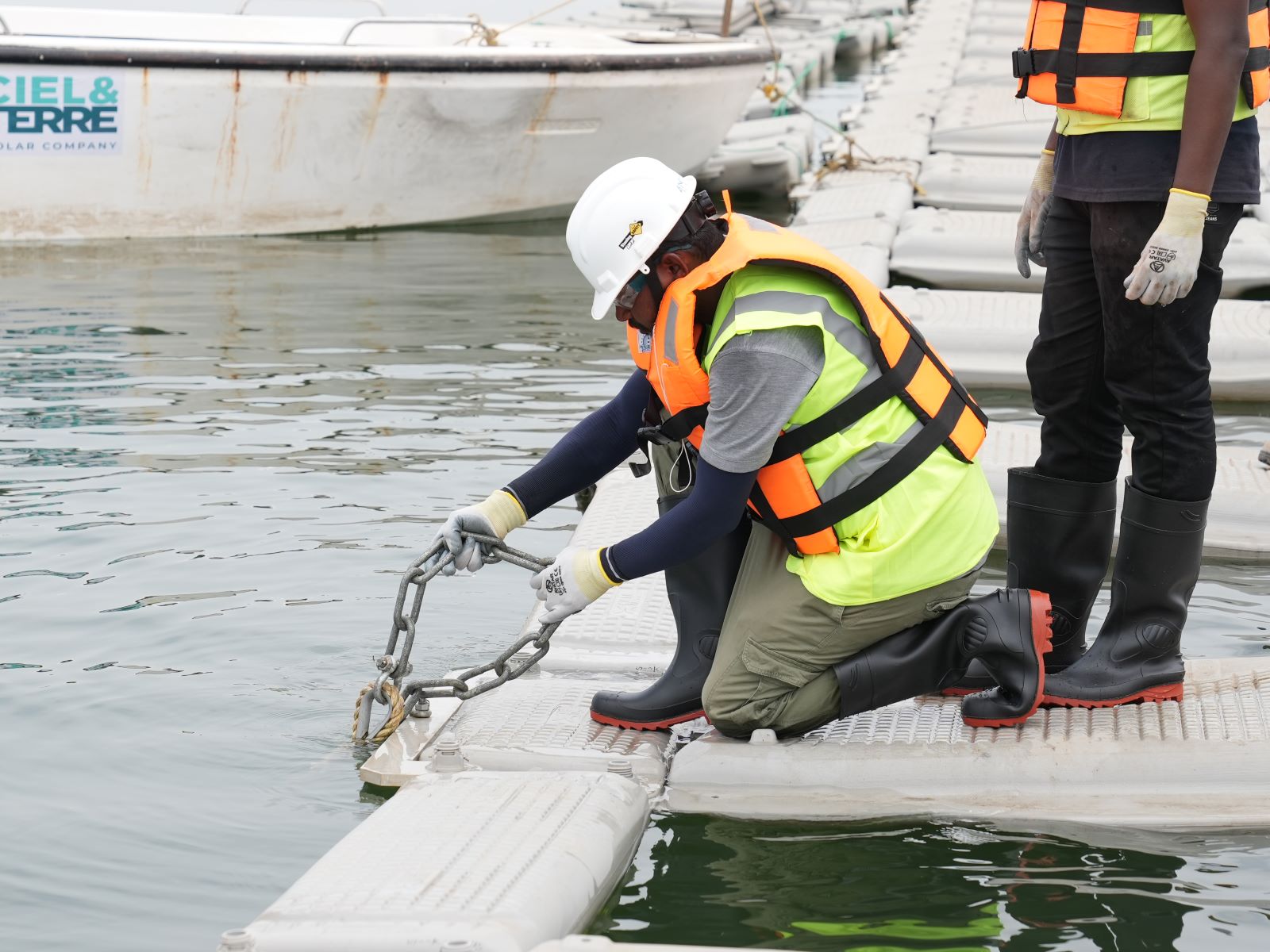

Monitoring and maintenance: ensuring long-term performance
Even the most robust anchoring systems for floating PV require regular monitoring. At Ciel & Terre, we have integrated anchoring inspection and monitoring into our maintenance services.
Our approach includes:
- Identifying wear or corrosion on mooring line components,
- Verifying the stability of anchoring points,
- Reacting quickly after extreme weather events.
We’ve implemented preventive monitoring protocols, including annual inspections and checks before and after major storms, to detect any platform drift early. This proactive strategy helps prevent production interruptions and extends the lifespan of the floating solar installation.
The success of a floating solar power plant is built on solid foundations—literally. The anchoring success factors for floating PV revolve around:
- Rigorous site analysis,
- Site-specific, standards-based design,
- Durable material selection,
- And proactive monitoring and maintenance.
An effective anchoring system ensures the stability, safety, energy performance, and long-term viability of the project. It is the key to optimized return on investment and reliable operation over decades.
By Chloé, marketing







